
A piezo buzzer exhibits a reasonably linear relationship between the input drive signal strength and the output audio power while a magnetic buzzer's audio output declines rapidly with a decreasing input drive signal. The frequency of the sound produced by both magnetic and piezo buzzers can be controlled over a wide range by the frequency of the signal driving the buzzer.
#Safe current for arduino piezo series
A piezo buzzer is modeled as a capacitor while a magnetic buzzer is modeled as a coil in series with a resistor. Construction of a typical piezo buzzerĪ piezo buzzer differs from a magnetic buzzer in that it is driven by a voltage rather than a current.
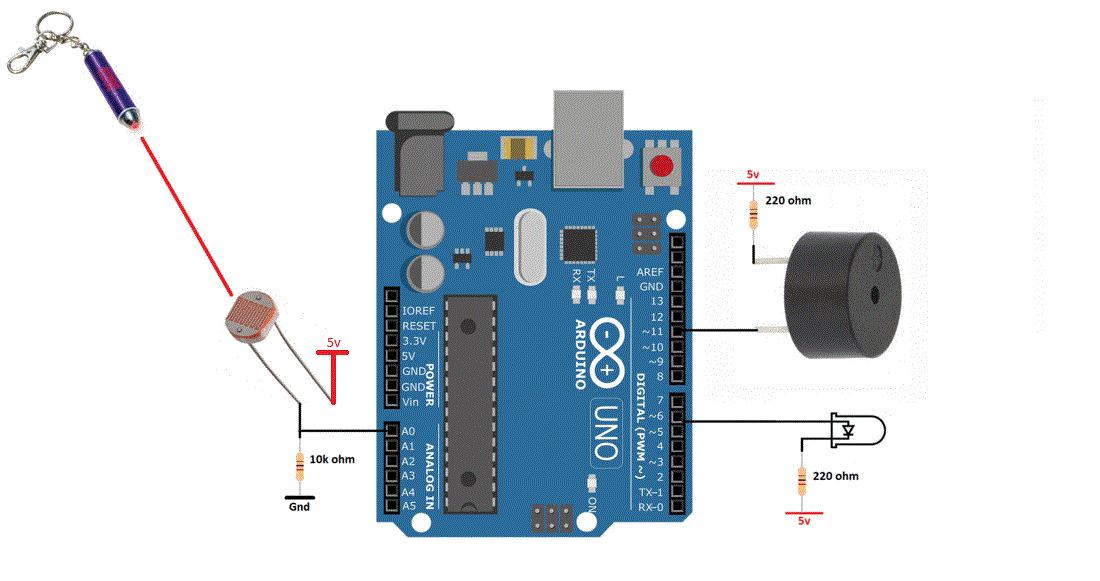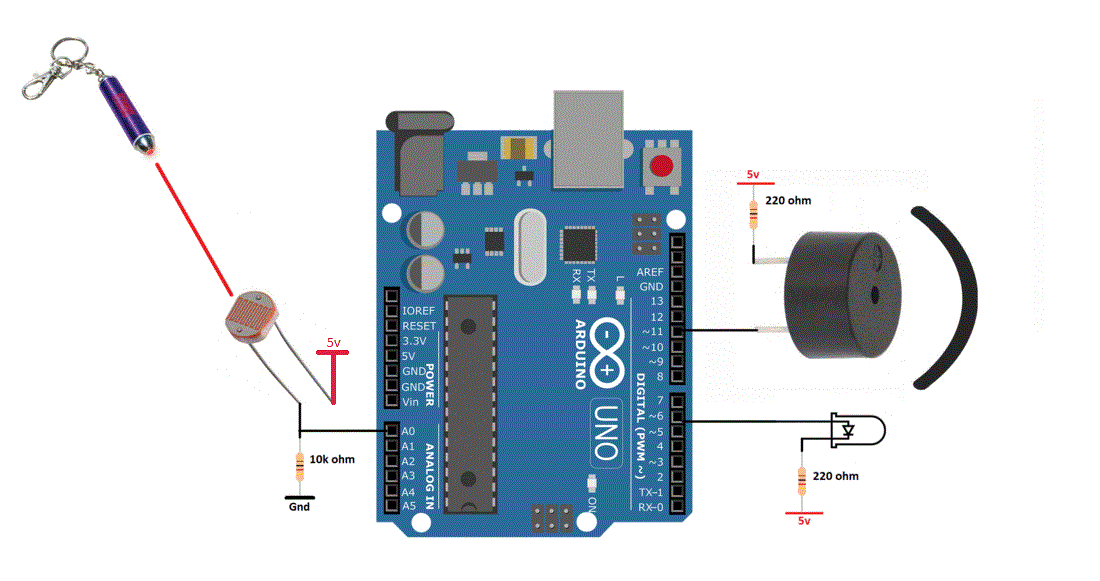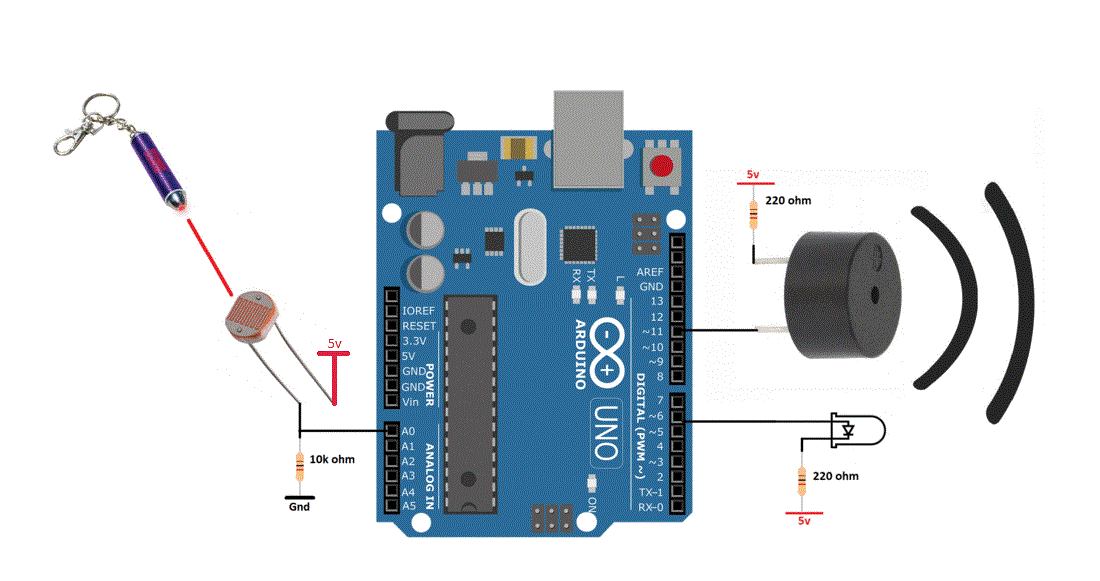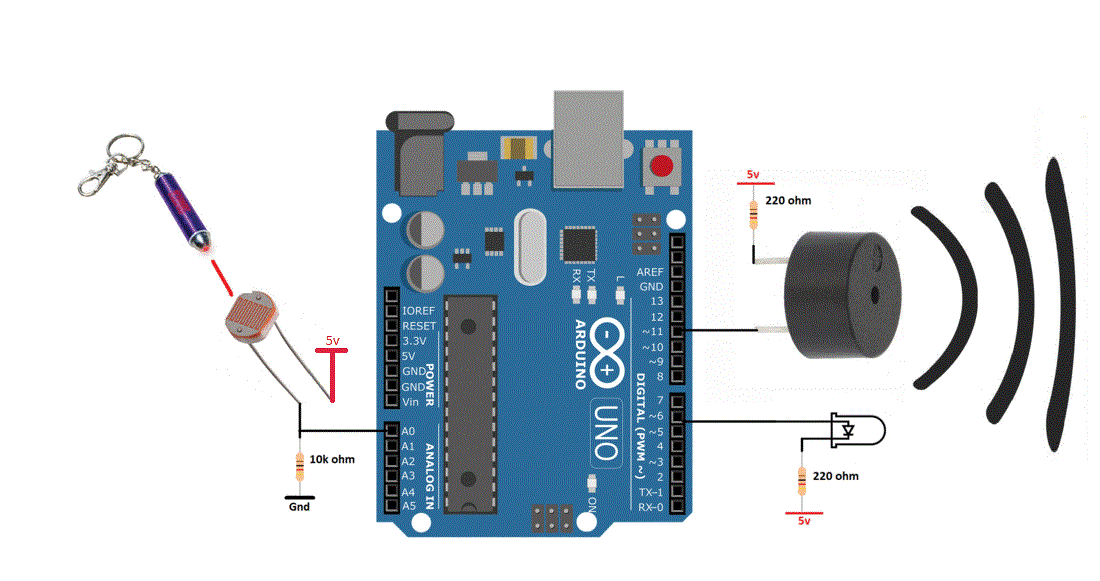

This movement of the piezo disk within the buzzer creates sound in a similar manner as the movement of the ferromagnetic disk in a magnetic buzzer or the speaker cone mentioned above. When a voltage is applied across the two electrodes, the piezoelectric material mechanically deforms due to the applied voltage. Piezo buzzers are constructed by placing electrical contacts on the two faces of a disk of piezoelectric material and then supporting the disk at the edges in an enclosure. Piezo buzzers are used in similar applications as magnetic buzzers. Construction of a typical magnetic buzzer The current through the coil is determined by the applied voltage and the impedance of the coil. A magnetic buzzer is a current driven device, but the power source is typically a voltage. The sound from a magnetic buzzer is produced by the movement of the ferromagnetic disk in a similar manner to how the cone in a speaker produces sound. A flexible ferromagnetic disk is attracted to the coil when the current is present and returns to a "rest" position when the current is not flowing through the coil. In a magnetic buzzer, a current is driven through a coil of wire which produces a magnetic field. However, it should be noted that the greater SPL available from piezo buzzers requires larger footprints. Magnetic buzzers operate at lower voltages and higher currents (1.5~12 V, > 20 mA) compared to piezo buzzers (12~220 V, < 20 mA), while piezo buzzers often have greater maximum sound pressure level (SPL) capability than magnetic buzzers. Many applications use either a magnetic or a piezo buzzer, but the decision regarding which of the two technologies to use is based upon many different constraints. The two most common technologies used in buzzer designs are magnetic and piezo. Understanding some of the technologies and configurations of buzzers is useful during the design process, so in this blog post we will describe typical configurations, provide example buzzer tones, and present common drive circuit options. One of the most common choices for audio communication is a buzzer. There are many choices for communicating information between a product and the user.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
